🏭 Introduction: From Disco to Dominance
1. The Evolution of Polyester
In my 20 years managing textile production, I have seen polyester transform from the shiny, uncomfortable “disco fabric” of the 1970s into the most versatile fiber in the modern world. Today, polyester fabric clothing dominates everything from high-performance athletic wear to durable industrial uniforms.
2. The Answer is Rarely Simple
However, many buyers still ask: “What is polyester made of?” or “Is polyester breathable?” The answer depends on three key factors:
- 🧵 Yarn Type: Spun vs. Filament
- 🧪 Finish: Wicking vs. DWR (Durable Water Repellent)
- 🏗️ Construction: Weave tightness and density
3. A Real-World Lesson
“I’ve seen clients reject a 100 polyester mens shirt for being ‘too hot’ because they chose a flat filament yarn instead of a textured, wicking one.”
📘 What You Will Learn
This guide is your technical manual. We will move beyond the basic definition of synthetic polyester to explore its fibre structure, compare it to cotton, and provide the exact PO spec sheets and testing standards you need to source it safely.
🧪 What Is Polyester Fabric? (Definition)

1. The Chemical Core
It is a category of polymers that contain the ester functional group in their main chain. In the textile industry, “polyester” almost always refers to Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET).
2. Engineered, Not Grown
It is a synthetic polyester material, meaning it is man-made, not grown like cotton or wool. Because it is engineered, polyester characteristics can be tailored:
- ✨ It can be made shiny or dull.
- 📏 It can be made stretchy or rigid.
- 💧 It can be made waterproof or absorbent.
3. Common Questions
It is 100% synthetic.
Naturally, no. But with modern moisture-wicking finishes and microfiber construction, breathability of polyester can rival cotton.
⚗️ What Is Polyester Fabric Made Of? (Composition)
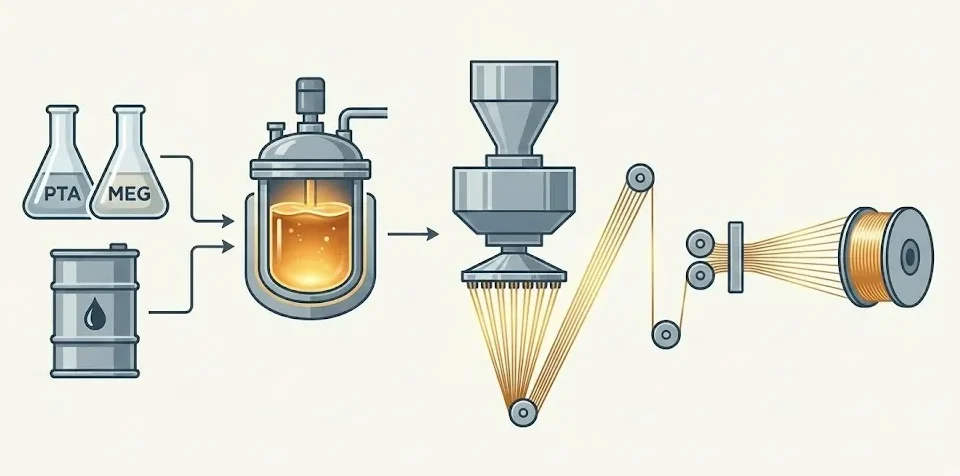
1. The Chemistry: It Starts with Petroleum
What is in polyester fabric? The journey begins with crude oil derivatives.
- 🛢️ Raw Materials: Purified Terephthalic Acid (PTA) and Monoethylene Glycol (MEG).
- 🔥 Polymerization: These chemicals are heated to form a molten polymer (PET).
- 🚿 Extrusion: The honey-like liquid is forced through a spinneret (like a showerhead) to create long strands called filaments.
- 💪 Drawing: These filaments are stretched to align the polyester fibre structure, giving it incredible strength.
2. Recycled Polyester (rPET)
Recycled polyester fabric is chemically identical but sourced differently. Instead of crude oil, we melt down used plastic bottles (post-consumer waste).
3. Industry Data
Recycled polyester now accounts for over 15% of the total polyester market.
🌱 Impact: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions by approximately 30-50% compared to virgin polyester.
🖐️ What Does Polyester Feel Like? (Texture/Appearance)
What does polyester fabric feel like? It depends entirely on how the yarn is processed.
1. Filament (FDY)
Texture: Smooth, slick, and cool to the touch.
🧥 Think of: A silky lining or a windbreaker.
2. Textured (DTY)
Texture: Soft, fluffy, and cotton-like.
🧸 Think of: A fleece jacket or soft leggings.
3. Spun Polyester
Texture: Mimics cotton or wool. Short fibers are spun together to create a hairy, matte texture.
👕 Think of: A cheap t-shirt or industrial work pants.
✅ The Verdict: How does polyester feel?
It can feel like silk, wool, or cotton depending on the engineering.
🏗️ What Is Polyester Used For?
Polyester is the go-to choice when buyers prioritize the “Holy Trinity” of performance:
🛡️ Durability + 📐 Shape Retention + 🧼 Easy Care
🏃 Activewear & Athleisure
Jerseys, interlocks, mesh, warp knits.
Often DTY + Wicking Finish
👔 Uniforms & Workwear
Twills, blends (TC/CVC).
Anti-Wrinkle Finishes
🧥 Outerwear & Sports Jackets
Shells/liners, ripstop, brushed knits.
DWR (Water Repellent) Finishes
👗 Lining
Taffeta, pongee, satin.
Filament Woven (Smooth)
🏠 Home Textiles
Microfiber bedding, curtains, upholstery.
Abrasion & Pilling Controlled
🎒 Bags & Accessories
Oxford, ripstop, coated fabrics.
PU / PVC Coatings
📏 Key Specs of Polyester (GSM, Yarn Type, Weave, Width)
When sourcing, you cannot just say “Polyester.” You must define the specifications. Use this polyester fabric spec snapshot table as your starting point.
| End-use | Construction | Yarn suggestion | Typical GSM | Notes to control risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Performance T-shirt | Knit jersey | DTY filament | 120–180 | add pilling target + wicking test |
| Sports leggings | Knit interlock | DTY + elastane | 200–280 | recovery + spirality control |
| Windbreaker shell | Woven plain/ripstop | filament (FDY) | 60–120 | add DWR + tear strength |
| Uniform pants | Woven twill | filament or poly-cotton | 220–320 | abrasion + seam slippage |
| Lining | Woven taffeta/satin | filament FDY | 50–90 | anti-static finish often needed |
| Microfiber bedding | Woven/knit microfiber | microfiber filament | 90–160 | snagging + pilling control |
| Upholstery | Woven heavy | filament/spun | 250–450 | Martindale/Wyzenbeek required |
⚠️ Crucial Note on Width
Always specify “Usable Width.” A 60″ roll might only have 58″ of usable fabric due to pinholes at the selvage.
🏃 Is Polyester Breathable? Performance Q&A
1: Is polyester breathable?
By itself, no. Polyester absorbs <0.4% moisture, meaning sweat sits on the skin.
💧 However: High-end performance polyester uses capillary action (wicking) to pull moisture through the fabric to the surface, where it evaporates.
2: Does 100 percent polyester shrink?
Very little. Unlike cotton, polyester is heat-set during manufacturing. Unless you wash it above 180°C (which is impossible at home), it stays stable.
3: Does polyester bleed color?
Rarely. It is dyed using Disperse Dyes at high temperatures (130°C). The dye locks deeply into the molecule.
4: Does 100 percent polyester stretch?
- 🧵 Fiber: Polyester fibers have high modulus (stiffness). Without elastane (Spandex), woven polyester has very little stretch.
- 🧶 Knit: Knitted polyester stretches due to the loop structure, not the fiber itself.
5: Is it durable?
Durable polyester is legendary. It resists abrasion, chemicals, and UV light better than most natural fibers.
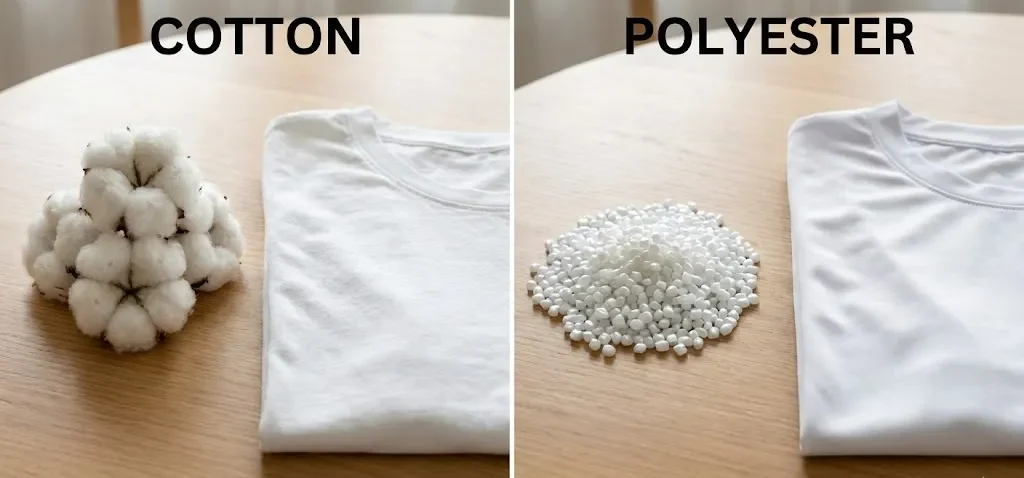
⚖️ Polyester vs Cotton: What’s the Difference?
The Primary Difference: Moisture Behavior
The primary difference is moisture behavior: cotton absorbs water, while polyester repels/doesn’t absorb much. This means polyester dries faster but can hold sweat on the skin unless the construction or finish is optimized.

| Topic | Polyester | Cotton |
|---|---|---|
| Drying speed | Fast | Slower |
| Wrinkle resistance | High | Lower |
| Shrink risk | Low (but heat sensitive) | Moderate (depends on finish) |
| Breathability feel | Construction-dependent | Generally better “natural” feel |
| Pilling risk | Can be high (spun/soft knits) | Usually lower (varies) |
| Price stability | Often more stable | Can vary by crop/grade |
🤝 Why Is Polyester Mixed with Cotton?
To get the best of both worlds.
Poly-Cotton (CVC or TC) blends offer the breathability of cotton combined with the strength and wrinkle resistance of polyester.
🔬 How to Test Polyester Quality? (AATCC/ISO/ASTM)
You cannot rely on “feeling” quality. You must test it.
| Risk you want to control | Recommended test | Common method families |
|---|---|---|
| GSM/weight consistency | GSM test | ASTM D3776 / ISO 3801 |
| Width & skew | width/skew measure | ASTM methods / ISO methods (specify your standard) |
| Wash shrinkage | laundering dimensional change | AATCC 135 / ISO 6330 |
| Colorfastness to washing | wash fastness | AATCC 61 / ISO 105-C06 |
| Crocking (rubbing) | dry/wet rubbing | AATCC 8 / ISO 105-X12 |
| Lightfastness | light exposure | AATCC 16.3 / ISO 105-B02 |
| Pilling | pilling grade | ASTM D3512 / ISO 12945-2 |
| Abrasion | durability wear | ASTM D4966 / ISO 12947 |
| Tensile (woven) | strength | ASTM D5034 / ISO 13934-1 |
| Tear (woven) | tear resistance | ASTM D1424 / ISO 13937-1 |
| Bursting (knits) | knit strength | ASTM D3786 / ISO 13938 |
| Air permeability | breathability | ASTM D737 / ISO 9237 |
| Seam slippage (woven) | seam opening | ASTM D434 / ISO 13936-2 |
💼 B2B Tip:
Choose tests based on end-use. Activewear buyers care about pilling + moisture management + recovery; upholstery cares about abrasion + snagging + seam slippage.
📊 Industry Standard
According to ISO standard 12945-2 for pilling, polyester fabrics—especially spun polyester—often require specific anti-pilling finishes to achieve a commercially acceptable Grade 3-4, as synthetic fibers are strong enough to anchor pills to the surface.
📝 What to write in the PO/spec sheet for polyester?
Copy-paste the template below (edit the brackets). This is where you “lock” the outcome.
Yarn type: [FDY / DTY / spun / microfiber / cationic]
Construction: [woven plain/twill/satin] or [knit jersey/interlock/pique]
GSM/Weight: [___ GSM] ± [3–5]%
Usable width: [___ cm/in] ± [1–2 cm]
Color: [Pantone/TCX/standard], shade band: [A/B/C] or “within approved swatch”
Lab dip / strike-off approval: required
Finish: [wicking / brushed / anti-static / DWR / anti-odor / heat-set]
Crocking dry/wet: ≥ []/[] (AATCC 8 / ISO 105-X12)
Wash fastness: ≥ [___] (AATCC 61 / ISO 105-C06)
Pilling: ≥ Grade [___] (ASTM D3512 / ISO 12945-2)
Abrasion: ≥ [___] cycles (ASTM D4966 / ISO 12947)
Packaging: roll length [], core ID [], face-to-face rolling [yes/no]
Bulk approval: PPS + TOP + shade continuity check required
🚫 Common Defects in Polyester & How to Avoid Them
📊 Typical MOQ, Lead Time & Cost Drivers
What buyers should expect in reality (beyond just the numbers).
📦 1. Typical MOQ Reality
- 🟢 Lowest MOQ / Fastest:Stock greige / Stock dyed. Material is already on the floor.
- 🟠 Medium MOQ:Custom color / Custom finish. MOQ increases because of dyeing vessel capacity and finishing line setup costs.
- 🔴 Highest MOQ / Longest Cycle:Custom yarn type (microfiber/cationic) or Special knit. Requires spinning new yarn or reconfiguring knitting machines.
⏳ 2. Lead Time Drivers
- ▸Yarn availability: (FDY / DTY / Microfiber)
- ▸Approvals: Lab dip / Strike-off rounds.
- ▸Production Queue: Finishing bottlenecks (DWR, brushing, heat setting).
- ▸QA Risk: Rework time (shade correction, pilling failures).
💰 3. Cost Drivers (Biggest Levers)
- $Yarn Type: (Microfiber / Cationic / ATY)
- $Construction: Complexity + GSM (Weight).
- $Route: Dye vs Print (Disperse vs Sublimation vs Solution-dyed).
- $Finishing: (Wicking, Anti-static, Anti-odor, DWR).
- $Tolerances: Width and quality (tight tolerances cost more).
🏁 Conclusion: The Workhorse of Textiles
What is polyester?
It is the workhorse of the textile world. Whether you need the rugged durability of durable polyester workwear or the soft touch of microfiber bedding, the key is specification.
❌ Don’t just order “Polyester.”
✅ Order “150D DTY Wicking Polyester.”
The difference is everything.
Ready to verify your specs?
🏭 Factory-Ready Quick Answers (FAQ)
☀️ Is polyester good for hot weather?
It can be, if you choose the right specs:
- Light GSM
- Breathable construction (mesh/looser knit)
- Moisture management finish
🖨️ Can polyester be sublimation printed?
Yes. Polyester is the industry standard for sublimation because disperse dye bonds well under heat.
💧 Is polyester waterproof?
No. Polyester is water-resistant by fiber nature, but true water performance depends on three extra factors:
- Weave density
- Coating/Lamination
- Seam construction
♻️ Is recycled polyester lower quality?
Not necessarily. rPET quality depends on filament uniformity, dye uptake stability, and process control.
💡 Sourcing Tip: Always ask for test reports and bulk shade consistency controls.